Natural Gas Basics
The main ingredient in natural gas is methane, a gas (or compound) composed of one carbon atom and four hydrogen atoms. Once the natural gas wells are drilled and completed gas flows up through the well to the surface of the ground and into large pipelines. Some of the gases that are produced along with methane, such as butane and propane (also known as “by-products”) are separated and cleaned at a gas processing plant. Because natural gas is colorless, odorless and tasteless, mercaptan (a chemical that smells like sulfur) is added before distribution, to give it a distinct unpleasant odor (it smells like rotten eggs).
How Natural Gas Is Used
Natural gas is used to produce steel, glass, paper, clothing, brick, electricity and as an essential raw material for many common products. Some products that use natural gas as a raw material are: paints, fertilizer, plastics, antifreeze, dyes, photographic film, medicines, and explosives.
Slightly more than half of the homes in the United States use natural gas as their main heating fuel. Natural gas is also used in the homes to fuel stoves, water heaters, clothes dryers, and other household appliances.
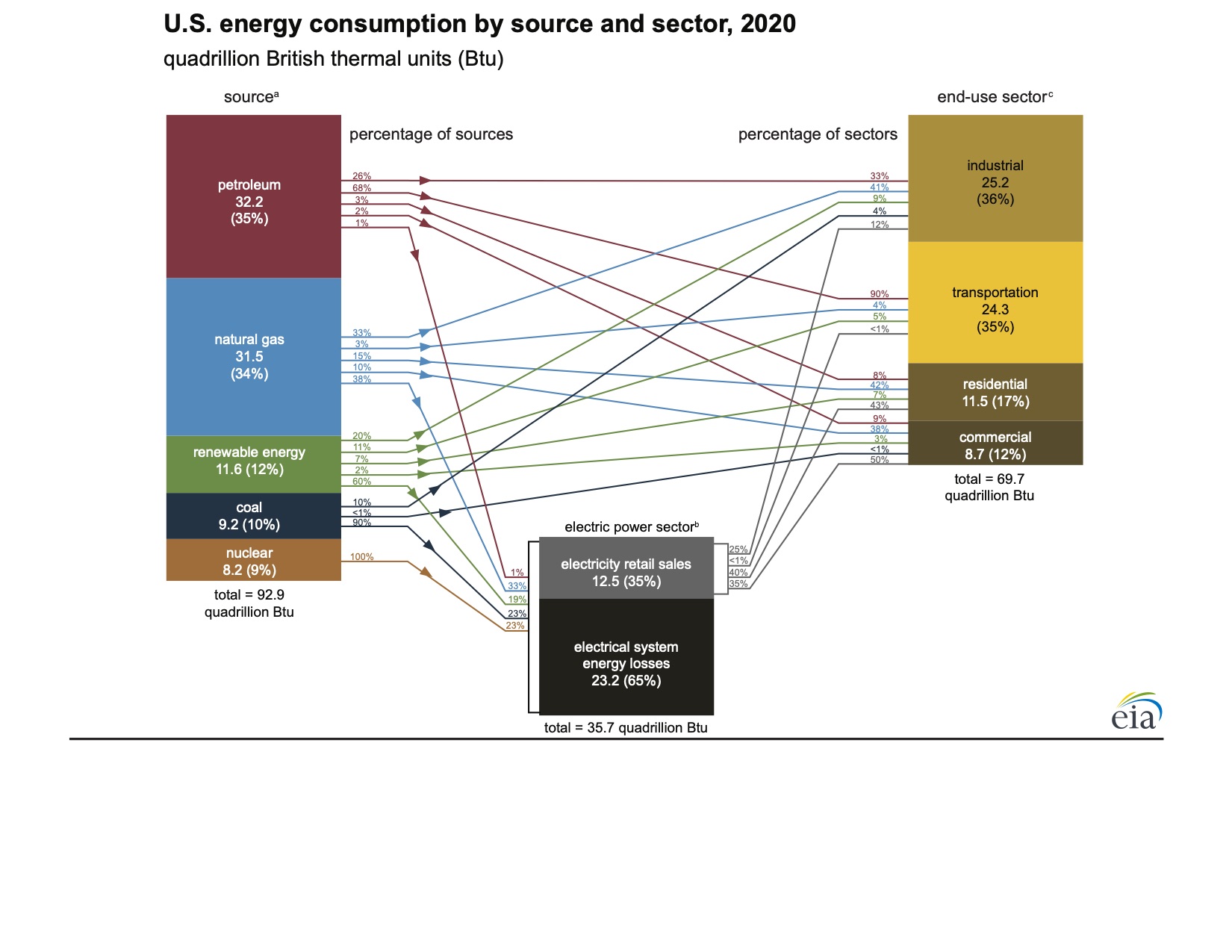
Natural Gas Is a Major Energy Source for the United States
In 2020, there were 483,326 natural gas wells producing in 34 different states. Each year thousands of new natural gas wells are drilled and competed in the U.S.A. About 34% of energy used in the United States came from natural gas in 2020. The United States used about 30.5 trillion cubic feet (Tcf) of natural gas in 2020.
Source: U.S. Energy Information Administration Natural Gas Monthly (April 2021)
Source: U.S. Energy Information Administration


